The term Localised Adiposity and Edematous Fibrosclerotic Panniculopathy (EFP) is just a more technical way of defining fat and cellulite. What are the differences between localised fat and cellulite?
Localised Adiposity and EFP: Types of fat and cellulite
Fat is an essential component of the human body.
There are 2 types of fat:
- Subcutaneous
- Visceral
Genetics play a fundamental role in fat, on how much there is, on the type of adipose cells and on localisation.
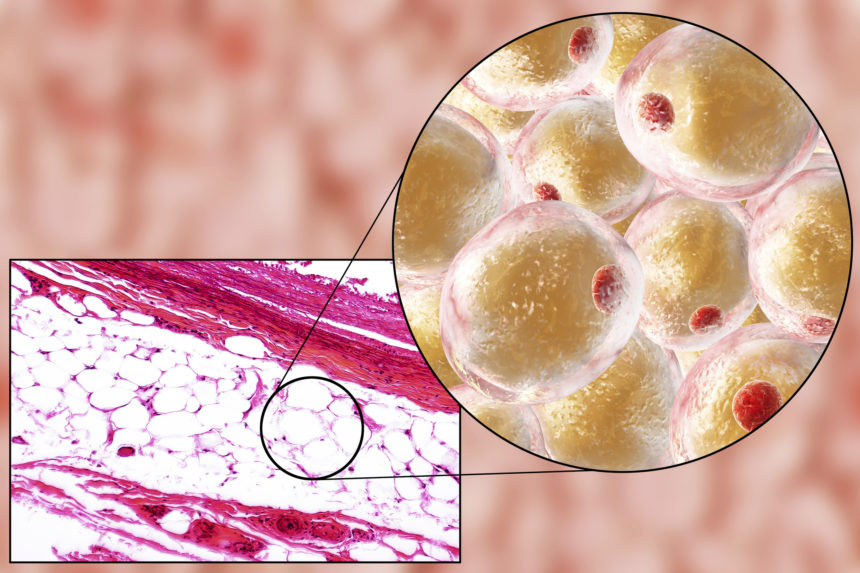
Subcutaneous fat is found in a layer just beneath the surface of the skin. It is a type of connective tissue, which contains:
- Blood vessels
- Nerves
- Adipocytes
Subcutaneous fat acts as an insulator for the body, helping to maintain a stable body temperature. Not only that, it is also a reserve of energy and physical protection against the external environment.
Visceral fat is the type of fat situated in the abdominal cavity, covering the vital organs. This type of fat accumulates deep under the muscle tissue in the abdomen; visceral fat is much more than a storage depot.
Localised Adiposity and EFP often coexist
Cellulite is therefore nothing more than fat with a dimpled appearance which appears just below the surface of the skin around the hips, thighs and buttocks.
Even thin people can have cellulite.
Cellulite is more pronounced when the connective tissue that separates the fat cells thickens, and it is more common in women. The fat cells have increased in volume and are held downwards by the fibrous septae; these pull, giving the skin the orange peel appearance.
Cellulite becomes more apparent with age because the skin is less toned and thinner.
Localised Adiposity and EFP. Is fat bad for health?
Cellulite is not harmful. Many people, however, would like to get rid of it because of its appearance.
Visceral fat is what poses more serious health problems.
Excessive visceral fat disrupts the hormonal balance in the body, with consequences for health such as:
- Hardening of the arteries
- Increase in blood pressure
- Impaired ability to use insulin
- Increase in the level of bad cholesterol, while the level of good cholesterol drops.
Localised Adiposity, EFP: Every fat has its exercise
Regular physical exercise can help prevent the accumulation of excess fat. For people who are prone to cellulite, physical exercise reduces the dimpled appearance of the skin because it improves peripheral circulation.
If you want to lose visceral or subcutaneous fat (subcutaneous fat is more difficult to eliminate) you should follow a balanced and healthy diet, accompanied by daily aerobic exercise and a workout 2 or 3 times a week. Having cellulite does not mean being overweight. Even thin people can have cellulite. However, if you are overweight, weight loss can improve cellulite.
Which exercises are best?
- Walking
- Jogging
Localised Adiposity and EFP: Improving the appearance of cellulite
Cellulite is nothing more than a particular aspect of fat under the skin. The fat appears irregular because it pushes against the connective tissue, causing the orange peel appearance. Physical exercise and diet can improve muscle tone and skin texture but do not have a direct action on cellulite.
Other factors that affect cellulite include:
- genetics
- poor diet
- diet rich in fats
- slow metabolism
- lack of physical activity
- hormonal changes
- dehydration
- total body fat
Localised Adiposity and EFP: Anti-cellulite treatments
There are many products and treatments that promise to eliminate cellulite on the thighs and buttocks. But there is no evidence that they are effective with long-term results.
Here are some treatments:
Mesotherapy. Mesotherapy can break down the fat and lead to an improvement in the appearance of cellulite. But it also involves risks, including swelling, infection and irregular contours.
Massages and well-being treatments. Massages and other well-being treatments can have a temporary effect on the appearance of the skin. But they do not eliminate cellulite. Any improvement is short-lived and is probably due to the draining action that reduces excess fluids.
Laser treatment. The FDA has authorised the use of a device that uses laser energy to treat cellulite. The treatment has contraindications that should be discussed with an expert doctor.
Combined treatments. There is a whole range of treatments which, when combined, work in synergy for limiting cellulite.
The list is not complete and many other treatments are available for improving the appearance of cellulite, such as ultrasound, radiofrequency, shock waves, cavitation, cryolipolysis, tissue stabilized guided subcision, etc.
Although the treatments promise to solve the problem, it is always best to start with a change of lifestyle (starting with physical activity, diet, eliminating smoking and alcohol, etc.). Experts agree that the most effective physical activity for cellulite is aerobic exercise, along with a diet rich in fruit, vegetables and fibre.